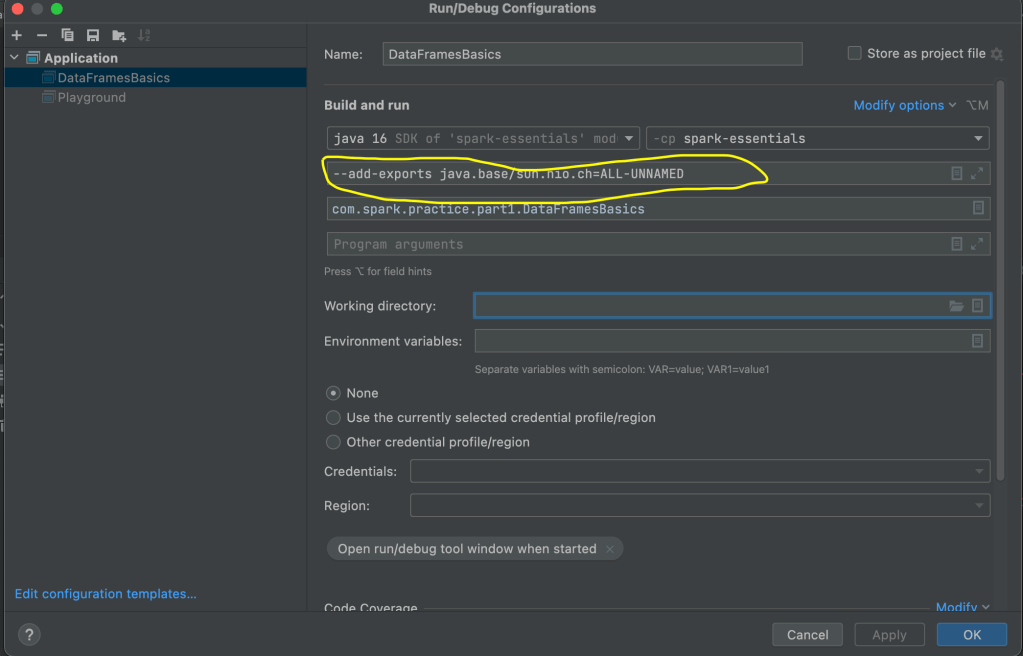
: add Java VM option --add-exports java.base/sun.nio.ch=ALL-UNNAMED
If you are getting this error with Intellij then add it to java vm option (select from Modify Option) list.

1. Create a new project
$ mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.xyz.myapp -DartifactId=MyApp -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DinteractiveMode=false
$ cd MyApp
2. To Build Package:
$ mvn package
//this will create target/MyApp-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
3. To Execute
$ java -cp target/MyApp-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.xyz.myapp
# Adding dependency to your project
Let say you wanted to add “json-simple” to your project:
add inside in the pom.xml file:
<dependency> <groupId>com.googlecode.json-simple</groupId> <artifactId>json-simple</artifactId> <version>1.1</version> </dependency>
– Now to execute a package with dependency you will have to include the path to the jar (I think there is a way to do it with pom.xml, but I don’t know this yet)
– This could complicated if you have multiple dependencies
– And also need to make sure you have the pkgs in the system where you want to deploy your code
– Solution: Create fat jar (a jar that includes all dependent jars, side effect: output file is bigger and takes longer to run ‘mvn package’ command)
– To create fat jar add this to your pom.xml inside :
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
<configuration>
<descriptorRefs>
<descriptorRef>jar-with-dependencies</descriptorRef>
</descriptorRefs>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>assemble-all</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Singleton in Java
Singleton is the design pattern that instantiate the class to one object.
Here is the example in java
public class JavaProject {
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("IN main class");
MYClass a = MYClass.mySingleFactory();
MYClass b = MYClass.mySingleFactory();
MYClass c = new MYClass(); //Avoid doing this if the class is to be used as Singleton, because this operation returns a new instance of MyClass
a.setI(1);
b.setI(2);
c.setI(3);
a.printI();
b.printI();
c.printI();
a.printI();
MYClass.mySingleFactory().printI(); //another way to call the singleton obj
}
}
public class MYClass {
private int i;
static MYClass inst;
public static MYClass mySingleFactory(){
if (inst == null){
inst = new MYClass();
}
return inst;
}
public void SingletonTest() {
System.out.println("SingletonTest constructor called");
}
public void printI(){
System.out.println("Value of I is: " + i);
}
public void setI(int i_){
i = i_;
}
}
Output:
IN main class
Value of I is: 2
Value of I is: 2
Value of I is: 2
Value of I is: 3
Value of I is: 2